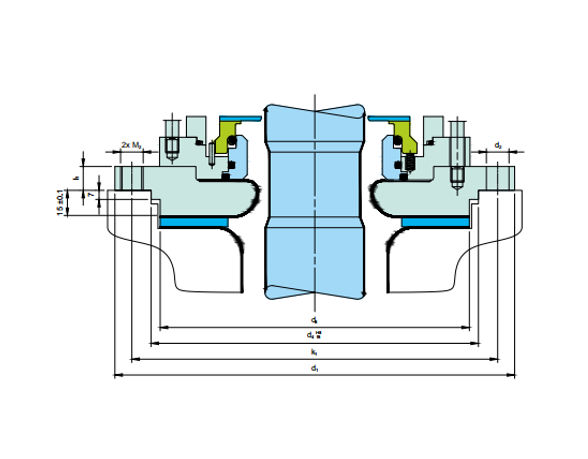
- Gas Lubricated Seals for Pumps & Agitators
GSAZ
- Dual seal configuration
- Balanced design
- Independent of direction of rotation
- Cartridge construction
- Gas-lubricated design
- Designed for top entry vessels
Download PDF
Details
-
1
Seal face(Diamond Coated), atmosphere side
-
2
Seal face (Q1), product side
-
6, 7
O-Ring
-
11
Seat (Q1)
-
17
Flange
-
22
Clamping ring
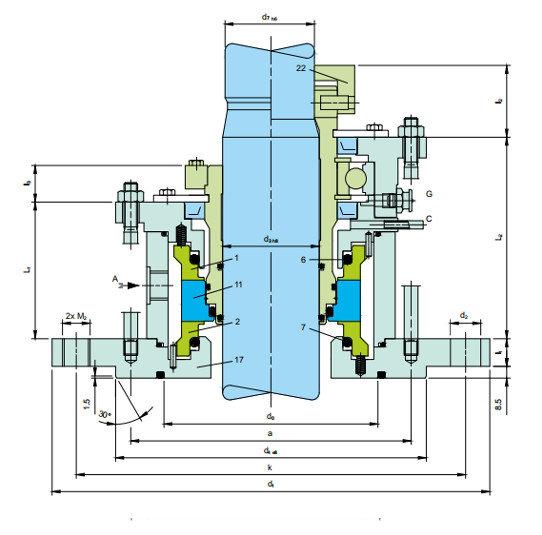
- Seal faces are designed to be noncontacting during operation
- Designed for environmental protection with high efficiency
- Due to non-contacting design there is no friction on the seal faces and there is no heat generated at the seal or in the medium
- Trouble free operations as complex components are not required to dissipate frictional heat
- To accommodate large axial movement torque transmission is through clamping ring
- Rotating seat is designed and arranged in the center
- Agitators
- Chemical industry
- Environmental harmful media with double seals
- Food and beverage industry
- Gases and liquids
- Media which require high purity
- Pharmaceutical industry
- Shaft diameter: d3 = 40 … 220 mm (1.6″ … 8.7″) Pressure p1 = vacuum … 6 bar (87 PSI), Δp = min. 3 bar (44 PSI), p3 = 9 bar (131 PSI)
- Temperature: t1 = -20 °C … +150 °C (-4 °F … +302 °F), with cooling flange 250 °C (482 °F)
- Speed = 0 … 10 m/s ( 0 … 33 ft/s
- Options:
- Cooling or heating flange
- Flush
- Polymerization barrier
- DIN 28136 T2 (for steel vessels)
- DIN 28141 (flange connection for steel vessels)
- DIN 28154 (shaft end for steel vessel)
- DIN 28136 T3 (for glass-lined vessels)
- DIN 28137 T2 (flange connection for glass-lined vessels)
Other products
-

U300N
Single seal configuration, Unbalanced Design, Dependent of direction of rotation, For plain shafts
Learn more
-

U200N
Single seal configuration, Unbalanced Design, Dependent of direction of rotation, For plain shafts…
Learn more
-

UG943
Single seal configuration, Unbalanced design, Independent of direction of rotation, For plain…
Learn more
-

UR-D
Dual seal configuration, Unbalanced design, Independent of direction of rotation…
Learn more